American Indians in Alabama
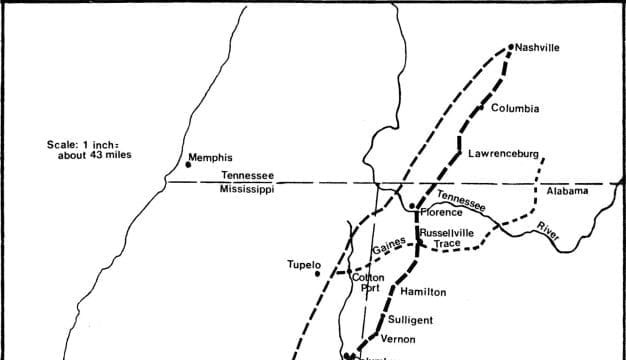
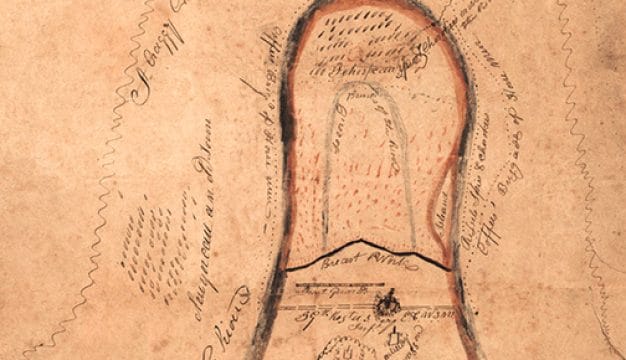
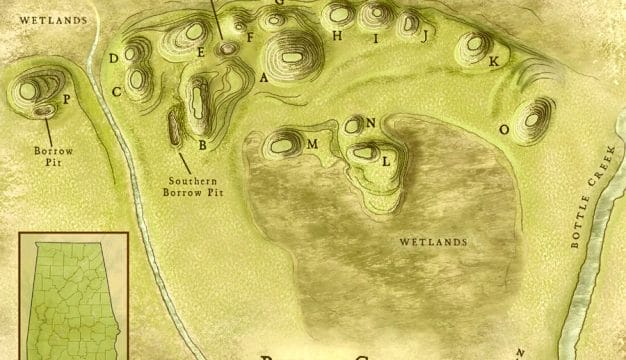
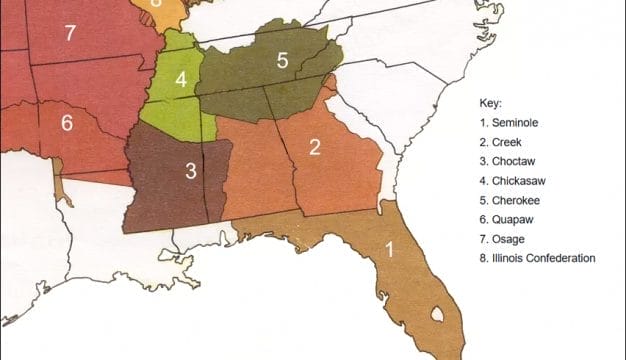
Alabama's indigenous history can be traced back more than 10,000 years, to the Paleoindian Period. Cultural and technological developments brought changes to the societies that inhabited what is now Alabama, with the most visible evidence of those changes being the remarkable earthen mounds built by the Mississippian people throughout the Southeast, in Alabama most notably at Moundville. By the time European fortune hunters and colonialist explorers arrived in the sixteenth century, the Indian groups in the Southeast had coalesced into the cultural groups known from the historic period: the Cherokees, Choctaws, Creeks, and Chickasaws, and smaller groups such as the Alabama-Coushattas and the Yuchis. As more Europeans and then U.S. settlers flooded into the Southeast, these peoples were subjected to continual assaults on their land, warfare, the spread of non-native diseases, and exploitation of their resources. In the 1830s, the majority of the Native Americans in Alabama were forced from their land to make way for cotton plantations and European American expansion. Today, the MOWA Band of Choctaw Indians and the Poarch Band of Creek Indians maintain their traditions on portions of their tribal homelands in the state.